🛑 Injunctions – Legal Protection Through Court Orders
Injunctions are powerful legal remedies used to prevent harm, protect rights, and maintain status quo in civil, commercial, or property-related disputes. Whether you're seeking to stop a construction, prevent breach of contract, or restrain unlawful activity, TAXAJ's legal experts assist you in filing or defending injunctions swiftly and effectively.
🔍 What is an Injunction?
An injunction is a judicial order granted by a civil court that either restrains a person from doing a particular act (prohibitory injunction) or compels them to perform a specific act (mandatory injunction). It is a type of equitable relief, aimed at preventing irreparable harm, protecting legal rights, and preserving the status quo until a final decision is made.
Injunctions are commonly used in situations where monetary compensation alone is not sufficient to undo or prevent the harm caused.
Injunctions are governed by:
The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 (Order 39)
The Specific Relief Act, 1963
Applicable special statutes (IPR laws, environmental laws, etc.)
Injunctions are commonly used in situations where monetary compensation alone is not sufficient to undo or prevent the harm caused.
Injunctions are governed by:
The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 (Order 39)
The Specific Relief Act, 1963
Applicable special statutes (IPR laws, environmental laws, etc.)
🧾 Example of an Injunction in a Property Dispute:
Scenario:
Mr. Sharma owns a residential plot in Delhi. One day, he discovers that his neighbor, Mr. Verma, has started illegal construction that extends into Mr. Sharma’s plot.
Legal Action:
Mr. Sharma immediately approaches the civil court and files a suit for injunction, seeking to restrain Mr. Verma from continuing construction until the ownership and boundaries are clearly determined.
Court's Order:
The court, after reviewing the documents (property papers, site map, photos) and finding a prima facie case, grants a Temporary Injunction under Order 39 of the Civil Procedure Code. It directs Mr. Verma to stop construction immediately and maintain the status quo until the case is resolved.
✅ Outcome:
Mr. Sharma's property is protected from further encroachment.
Mr. Verma is legally restrained from continuing the act.
If Mr. Verma violates the injunction, he can face Contempt of Court proceedings.
This is a typical use of an injunction to prevent irreparable harm and maintain legal and physical status quo during a pending dispute. Injunctions are commonly used in property, IP, business, and family law cases where time is critical.
📂 Types of Injunctions
Injunctions are classified based on their purpose, timing, and nature of relief granted by the court. Understanding these types helps you choose the right legal strategy when seeking or defending against one.
1️⃣ Temporary (Interim) Injunction
A Temporary Injunction is granted during the pendency of a case to preserve the status quo and prevent ongoing or potential harm until a final decision is made.
✅ Key Features:
Granted under Order 39 Rules 1 & 2 of the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC), 1908
Can be ex parte (without notice to the other party) in urgent situations
Remains valid until the court gives a final verdict or issues further orders
📌 Example:
A builder starts construction on disputed land. The rightful owner seeks a temporary injunction to stop the activity while the ownership dispute is pending in court.
3️⃣ Mandatory Injunction
Unlike a prohibitory injunction (which stops something), a Mandatory Injunctioncompels the defendant to take a specific action—usually to undo a wrong or perform a legal duty.
✅ Key Features:
Granted under Section 39 of the Specific Relief Act, 1963
Harder to obtain; requires clear proof of wrongdoing and urgency
Used when mere restraint isn’t enough
📌 Example:
A person illegally builds a wall blocking your access to your home. The court issues a mandatory injunction directing the wall to be demolished and access restored.
4️⃣ Preventive Injunction
A Preventive Injunction is any order that aims to prevent a threatened wrong, especially in intellectual property, environmental, or reputational harm cases.
📌 Example:
Stopping a publisher from printing defamatory content about an individual.
5️⃣ Ad-Interim Injunction
This is a type of temporary relief granted immediately, even before the other party appears in court, usually in urgent ex-parte situations.
📌 Example:
An order to stop demolition of a house the very next morning, until the next hearing.
2️⃣ Permanent (Perpetual) Injunction
A Permanent Injunction is granted after full trial of the case. It permanently restrains the defendant from committing a wrongful act that infringes upon the plaintiff’s rights.
✅ Key Features:
Granted under Section 38 of the Specific Relief Act, 1963
Based on final findings and evidence
Legally binding and enforceable unless appealed
📌 Example:
A court permanently prohibits a business from using a brand name that infringes upon a registered trademark.

⚖️ Legal Grounds for Injunctions
Courts do not grant injunctions lightly. To obtain an injunction—whether temporary, permanent, or mandatory—the applicant must satisfy certain well-established legal criteria. These are designed to ensure that the court only intervenes in appropriate and urgent circumstances.
Here are the key legal grounds upon which courts grant injunctions:
1️⃣ Prima Facie Case
This means the applicant must demonstrate a reasonable basis for their legal claim—not necessarily a full-blown winning argument, but one strong enough to justify the court’s intervention.
✅ Example:
If a property owner has a registered title and someone is trying to encroach upon it, that establishes a prima facie case of ownership and the need for protection.
✅ Key Case:
Dalpat Kumar v. Prahlad Singh, (1992) 1 SCC 719
The Supreme Court held that a mere chance of success in the suit is not sufficient; there must be a serious question to be tried.
3️⃣ Balance of Convenience
This means the court will weigh the hardship to both parties. If granting the injunction causes less inconvenience to the defendant than denying it would to the applicant, the balance tips in favor of the injunction.
✅ Example:
Stopping illegal construction might inconvenience the builder, but not stopping it may permanently deprive the rightful owner of their land.
✅ Key Case:
M. Gurudas v. Rasaranjan, (2006) 8 SCC 367
The Court stated that the inconvenience which the injunction would cause to the defendant must be less than that which denial would cause to the plaintiff.
4️⃣ Clean Hands Doctrine
The applicant must come to court with honest intentions and must not have engaged in any fraud, suppression of material facts, or illegal behavior themselves. Courts refuse injunctions to those who are guilty of misconduct in the same matter.
✅ Example:
If a party lies about the timeline of events or hides documents, they may lose the right to equitable relief like an injunction.
✅ Key Case:
Gujarat Bottling Co. Ltd. v. Coca Cola Co., (1995) 5 SCC 545
The Court reiterated that a person who seeks equity must do equity and must come with clean hands.
5️⃣ Urgency
Especially in temporary or ad-interim injunctions, urgency is a critical factor. The threat of harm must be imminent and substantial, not hypothetical or long-term.
✅ Key Case:
K.K. Modi v. K.N. Modi, (1998) 3 SCC 573
Delay in seeking injunction relief was viewed as suggestive of lack of urgency and reduced entitlement to equitable relief.
2️⃣ Irreparable Injury
The applicant must show that they would suffer harm that cannot be adequately compensated by money if the injunction is not granted.
✅ Examples:
Loss of reputation or goodwill
Permanent damage to property
Exposure of trade secrets
Destruction of evidence
✅ Key Case:
Best Sellers Retail (India) Pvt. Ltd. v. Aditya Birla Nuvo Ltd., AIR 2012 SC 2448
The Court emphasized that irreparable injury must be actual and substantial, not speculative or imagined.

6️⃣ No Alternative Remedy
Injunctions are typically granted when there is no adequate alternative legal remedy available. If the loss can be compensated through damages alone, the court may deny the injunction.
✅ Key Case:
American Cyanamid Co. v. Ethicon Ltd., (1975) 1 All ER 504 (UK, followed in India)
It was held that damages must not be an adequate remedy if injunction is to be granted.
📌 Conclusion with Legal Authority
These legal principles—backed by authoritative case law—are central to any application for an injunction. At TAXAJ, we ensure every claim for injunctive relief is legally sound, properly supported, and strategically argued before the court.
🏛 Judicial Discretion
Even if all grounds are satisfied, injunctions are not granted as a matter of right. Courts exercise discretion based on the specific facts and equities of each case.
🧾 Common Situations Where Injunctions Are Used
Injunctions are crucial legal tools in situations where timely intervention by the court is required to prevent harm, preserve rights, or avoid injustice. Below are common scenarios where courts frequently grant injunctions:
🏡 1. Property Disputes
To stop illegal construction or encroachment on your land
To maintain possession when facing threats of forceful eviction
To restrain a neighbor or third party from interfering with easement rights
Example: A court halts unauthorized construction on disputed land until the title suit is resolved.
™️ 3. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
To stop unauthorized use of your trademark, brand name, logo, or design
To prevent the publication or distribution of pirated software, books, or media
To prohibit domain name squatting or similar deceptive trade practices
Example: A court bars a competitor from using a deceptively similar brand name.
🤝 4. Employment & Trade Secrets
To restrain ex-employees from soliciting clients or revealing confidential business information
To enforce terms of employment contracts or non-solicitation agreements
Example: A startup gets an injunction against a former employee who tries to leak pricing strategy to a rival.
📢 5. Defamation or Harassment
To prevent the publication of defamatory content in print, digital, or social media
To stop cyberbullying or blackmail through threatening posts or messages
Example: A court issues an order preventing a news outlet from airing unverified, damaging claims about a company.
🏛 6. Family & Matrimonial Disputes
To restrain the spouse from alienating joint property
To stop the sale or transfer of marital assets before divorce is finalized
Example: A wife secures an injunction preventing the husband from selling shared assets during divorce proceedings.
🌐 8. Digital & Online Content
To restrict the publication of confidential data, fake reviews, or defamatory material
To take down infringing content hosted on websites or social media
Example: A court orders a website to remove pirated movies violating copyright.
📄 2. Breach of Contract
To stop a party from violating terms of a commercial or service agreement
To enforce non-compete or confidentiality clauses in employment contracts
To prevent wrongful termination or execution of agreements under dispute
Example: A software vendor is restrained from sharing source code that belongs to the client.

💼 7. Company Law & Shareholder Disputes
To prevent a company from issuing shares to third parties without board approval
To stop removal of directors or misuse of funds pending legal challenge
Example: A minority shareholder obtains an injunction to stop dilution of shareholding.
🚧 9. Environmental & Public Interest Matters
To stop illegal mining, deforestation, or construction in eco-sensitive zones
To halt government or private projects without necessary approvals
Example: An environmental NGO gets a stay on construction violating pollution norms.
📌 Need Immediate Legal Relief?
At TAXAJ, our litigation team specializes in urgent injunctions across industries—from IP to real estate. Contact us today for strategic advice and court representation.
⚠️ Consequences of Violating Injunction Orders
An injunction is a binding court order, and disobeying it is not only a legal breach but also a serious contempt of court. The consequences can be both civil and criminal in nature, depending on the severity and intent.
1️⃣ Contempt of Court Proceedings
Violating an injunction order is treated as civil or criminal contempt under the Contempt of Courts Act, 1971.
🛑 Civil Contempt: Willful disobedience of a court order
🚨 Criminal Contempt: Actions that scandalize or lower the authority of the court
Punishment:
Up to 6 months imprisonment
Fine up to ₹2,000, or both
📌 Case Law:
Ashok Paper Kamgar Union v. Dharam Godha, (2003) 11 SCC 1
Supreme Court held that wilful disobedience of injunctions undermines the administration of justice and must be dealt with strictly.
3️⃣ Adverse Legal Orders
Violation can result in:
Striking off of pleadings
Dismissal of defenses
Decree or judgment in favor of the other party
Example: In property disputes, disobedience can lead to automatic eviction orders or denial of legal rights.
4️⃣ Loss of Legal Credibility
Courts view willful non-compliance with extreme seriousness. The violator may lose moral and legal standing in all related matters.
5️⃣ Police Action & Enforcement
In certain cases, especially those involving public safety or serious rights violations, courts may direct the local police to enforce the injunction, including seizure of assets or arrest.
2️⃣ Monetary Penalties & Damages
Courts may award compensatory damages to the aggrieved party who suffers loss due to the violation of an injunction.
Example: If a builder ignores a stop-work injunction and completes illegal construction, they may be ordered to pay damages or demolish the structure.

🧑⚖️ Bottom Line:
Disregarding an injunction isn’t just a procedural error—it’s a serious punishable offence that could lead to penalties, imprisonment, and permanent legal setbacks. Always comply or approach the court for modification or clarification.
📌 Pro Tip:
Injunctions are discretionary reliefs. Courts will only grant them if you're quick to act, and your claim is well-documented and legally valid.
🏛 Need Urgent Relief?
Contact TAXAJ’s legal team to initiate or contest an injunction with strategic legal backing. We help protect your interests—before damage is done.
📋 Checklist Before Filing for Injunction
Filing for an injunction requires thoughtful preparation. Below is a comprehensive checklist to ensure your application is legally sound, urgent, and well-documented:
✅ 1. Establish Prima Facie Case
Do you have strong legal grounds or ownership/documentary rights?
Is there a genuine dispute that needs urgent intervention?
🔎 Tip: Consult legal counsel to verify if your case has merit before filing.
✅ 3. Prove Urgency
Is the harm imminent or ongoing?
Have you approached the court without unnecessary delay?
📅 Note: Courts may refuse relief if there's a significant delay or no urgent threat.
✅ 4. Gather Supporting Documents
Ownership or contract documents
Photographic/video evidence
Communications (emails, notices, threats)
Past orders, if any
🗂️ Important: Documents must support both factual and legal claims.
✅ 5. Identify the Right Forum
Is it a civil court, NCLT, High Court, or special tribunal?
Do you need to approach a specific court with jurisdiction over the dispute?
📍 Example: NCLT for company disputes; Civil Court for property or contract matters.
✅ 7. Review the Clean Hands Doctrine
Have you disclosed all material facts?
Are you free from wrongdoing in the matter?
⚠️ Warning: Courts may deny relief if you mislead or suppress information.
✅ 9. Estimate Costs & Timeline
Filing fees, lawyer fees, and documentation costs
Understand the legal process and possible timelines involved
📈 Tip: A temporary injunction can be filed quickly, but permanent relief takes time.
✅ 10. Prepare a Draft of the Plaint & Affidavit
Clearly state facts, legal grounds, urgency, and relief sought
Include all annexures, evidence, and verification
✍️ Final Step: Review everything with a legal expert to avoid rejection or delays.
✅ 2. Demonstrate Irreparable Injury
Can the harm you're facing not be compensated in money?
Will delay in court relief result in permanent loss or injustice?
📌 Example: Loss of property rights, business secrets, or personal liberty.

✅ 6. Check for Pre-Suit Requirements
Have you issued a legal notice (if required)?
Is mediation or arbitration needed before court action (contract clause)?
📜 Tip: Fulfilling pre-litigation requirements boosts your credibility in court.
✅ 8. Decide Type of Injunction Sought
🔒 Temporary Injunction (to maintain status quo)
🚫 Prohibitory Injunction (to stop an act)
🛠️ Mandatory Injunction (to compel action)
🕒 Ad-Interim Injunction (emergency short-term relief)
🧑⚖️ Need Help?
TAXAJ’s Litigation Experts help clients prepare watertight injunction applications, from drafting pleadings to appearing before the court.
📑 Documents Required to File an Injunction
When seeking an injunction, courts require clear and convincing evidence to assess the urgency, merit, and legality of your claim. Below is a checklist of key documents typically required to support your injunction application:
1️⃣ Proof of Legal Right or Ownership
Documents establishing your legal standing or entitlement in the matter:
Property title deeds, lease agreements, or sale deeds
Partnership agreements, shareholder records
Intellectual property registration certificates
Contracts, MOUs, or service agreements
📌 Why Needed? To show that your right is being violated or is at risk.
3️⃣ Urgency & Harm Evidence
Photographs or videos showing construction, damage, encroachment, etc.
Letters or communication showing imminent risk
Medical, environmental, or technical reports, if applicable
📍 Demonstrates “irreparable harm” if the injunction is not granted.
4️⃣ Supporting Affidavit
A notarized affidavit affirming the facts of your case and the necessity for relief.
✍️ This is a sworn legal document that adds weight to your case.
5️⃣ List of Respondents/Opposite Parties
Full names, addresses, and legal status (individual, firm, company) of all parties against whom the injunction is sought.
🧾 Helps the court issue notice and decide jurisdiction.
6️⃣ Copy of Previous Legal Correspondence (if any)
Legal notices exchanged
Settlement attempts
Previous orders from any court or authority
📜 Shows you tried to resolve the matter amicably or have past legal context.
🧑⚖️ Final Note:
Incomplete or poorly supported injunction filings are often denied or delayed. At TAXAJ, we help clients compile, draft, and file strong injunction applications with court-ready documentation.
2️⃣ Cause of Action Documents
Details of the dispute and how your rights are being infringed
Emails, text messages, legal notices, or WhatsApp chats
Screenshots, social media posts, or media coverage
📎 Supports your narrative of the threat or wrongful action.
7️⃣ Draft of the Petition or Plaint
Includes:
Statement of facts
Grounds for injunction
Relief sought
Index of documents and annexures
📄 A complete and well-structured plaint ensures faster hearing and relief.
🕒 Timeline for Injunction Matters
The timeline for injunction matters can vary depending on the urgency, type of injunction, and court workload, but here's a general outline of how it progresses:
🔹 1. Filing of Application & Affidavit
⏱️ Timeframe: Day 1
Drafting and filing the injunction petition along with the supporting affidavit and annexures
Filing is done before the appropriate Civil Court, High Court, or Tribunal depending on jurisdiction
🔹 3. Ad-Interim (Temporary) Injunction
⏱️ Timeframe: Within 1–5 Days
If the court is satisfied with the urgency and evidence, it may pass an ad-interim order even before hearing the opposite party
This helps prevent irreparable damage until the full matter is heard
🔹 4. Issuance of Notice to Opposite Party
⏱️ Timeframe: Within 7–15 Days
The court issues notice to the respondent(s) asking them to file a reply
Time to reply usually ranges between 7 to 30 days
🔹 5. Reply & Counter-Affidavit by Opposite Party
⏱️ Timeframe: 2–4 Weeks (or more depending on extensions)
The opposite party files their written reply with documents
Court may also grant time for rejoinder (your reply to their reply)
🔹 6. Final Hearing on Injunction
⏱️ Timeframe: 1–3 Months (may vary by court backlog)
After pleadings are complete, the court hears arguments
A detailed interim or permanent injunction order is passed after examining facts, urgency, and evidence
🔹 2. Mentioning & Urgent Hearing
⏱️ Timeframe: Same Day to 2 Days
If there is urgency (e.g., illegal construction, IP infringement), your counsel can mention the matter for urgent hearing
The court may take it up the same day or the next available day
📌 Factors Affecting Timeline:
Court’s calendar and case load
Opposite party’s delay in replying
Type of injunction (temporary/emergency vs. permanent)
Complexity of the matter
🧑⚖️ Need Fast Relief?
TAXAJ’s litigation team ensures well-drafted, properly supported injunction filings that can fast-track your chances of urgent relief.
💼 Industries Where Injunctions Are Common
Injunctions are not limited to personal or property disputes — they play a crucial role in protecting business interests across multiple sectors. Below are the key industries where injunctions are frequently used to safeguard rights, prevent loss, or stop unlawful acts:
🏗️ 1. Real Estate & Construction
Stay orders on illegal construction or land encroachment
Injunctions to prevent sale or transfer of disputed property
Protection against eviction or breach of lease agreements
📍 Common Parties Involved: Developers, landlords, tenants, buyers

🏥 5. Pharmaceutical & Healthcare
Patent injunctions to stop generic drug launches before expiry
Preventing misuse of brand names, formulas, or packaging
IP protection in R&D and clinical trial data
📍 Common Issues: Patent wars, brand identity misuse
⚙️ 7. Manufacturing & Industrial
Preventing misuse of machinery designs or trade secrets
Injunctions against breach of supply agreements
Halting construction or operations due to environmental or licensing issues
📍 Common Risks: Equipment duplication, environmental compliance
🧠 2. Technology & IT
Restraining ex-employees from misusing confidential code or algorithms
Protecting software IP or proprietary platforms from infringement
Blocking unauthorized use of domain names or trade dress
📍 Common Disputes: Source code theft, SaaS licensing violations
🛍️ 3. Retail, FMCG & E-commerce
Trademark injunctions to stop sale of counterfeit or similar branded goods
Restraining unauthorised sellers or distributors
Preventing false advertising or domain squatting
📍 Common Brands Involved: Consumer goods, apparel, electronics
🎬 4. Media & Entertainment
Blocking illegal streaming or piracy of content
Injunctions against publication of defamatory or unauthorized media
Protecting celebrity image rights and brand endorsements
📍 Common Cases: Movie releases, music rights, influencer contracts
💼 6. Corporate & Startups
Protecting shareholder rights in boardroom disputes
Stopping unauthorised issue of shares or dilution
Enforcing non-compete or non-solicit clauses
📍 Common Clients: Startups, joint ventures, angel investors
🏛️ 8. NGOs & Public Interest Litigation (PIL)
Environmental injunctions to stop deforestation, pollution
Restraining public works that violate citizens' rights or regulations
Halting unjustified government land acquisition or zoning changes
📍 Common Focus: Social rights, ecological preservation
🔐 Defending Against a False or Unfair Injunction
While injunctions are powerful legal tools, they can sometimes be misused by parties to delay, harass, or suppress legitimate business activity. If you’ve been served with a false, exaggerated, or unfair injunction order — you have legal remedies to defend yourself and protect your rights.
⚖️ 1. Challenge the Maintainability
Argue lack of prima facie case: Show the applicant has no substantial legal right.
Disprove urgency or irreparable harm: Demonstrate that the threat is not immediate or compensable in money.
Question jurisdiction: Prove the court is not the correct forum.
🧑⚖️ Outcome: The injunction can be vacated on preliminary legal grounds.

🧑⚖️ At TAXAJ:
We assist individuals and businesses in robustly defending against unjust injunctions by preparing strong responses, representing you in hearings, and seeking reversal or compensation where applicable.
📄 2. File a Detailed Reply & Counter-Affidavit
Refute each claim with evidence (contracts, records, timelines)
Attach photographs, emails, agreements, or affidavits disproving allegations
Assert your side clearly and highlight misleading or suppressed facts by the plaintiff
📌 Tip: A strong reply increases your chance of getting the order dismissed at the interim stage.
📢 3. Apply for Vacation or Modification of the Injunction
Move the court under Order XXXIX Rule 4 of CPC to set aside or modify the injunction
Argue that it was granted ex parte (without your version), or based on false/misleading information
📍 Example: If a business is wrongly restrained from using its own registered trademark.
💰 4. Seek Compensation for Wrongful Injunction
If the injunction has caused loss of business, reputation, or delays, you may be entitled to compensation or costs
Courts may impose damages on the party who abused the legal process
📎 Legal Basis: Section 95 of CPC allows compensation for frivolous/interim injunctions.
🚫 5. Expose “Clean Hands” Doctrine Violation
If the opposing party withheld facts or acted fraudulently, the court may dismiss their case entirely
The principle of “he who seeks equity must come with clean hands” applies strictly in injunction matters
📌 Case Law:K.K. Modi vs K.N. Modi & Ors (1998) – relief denied due to abuse of court process.
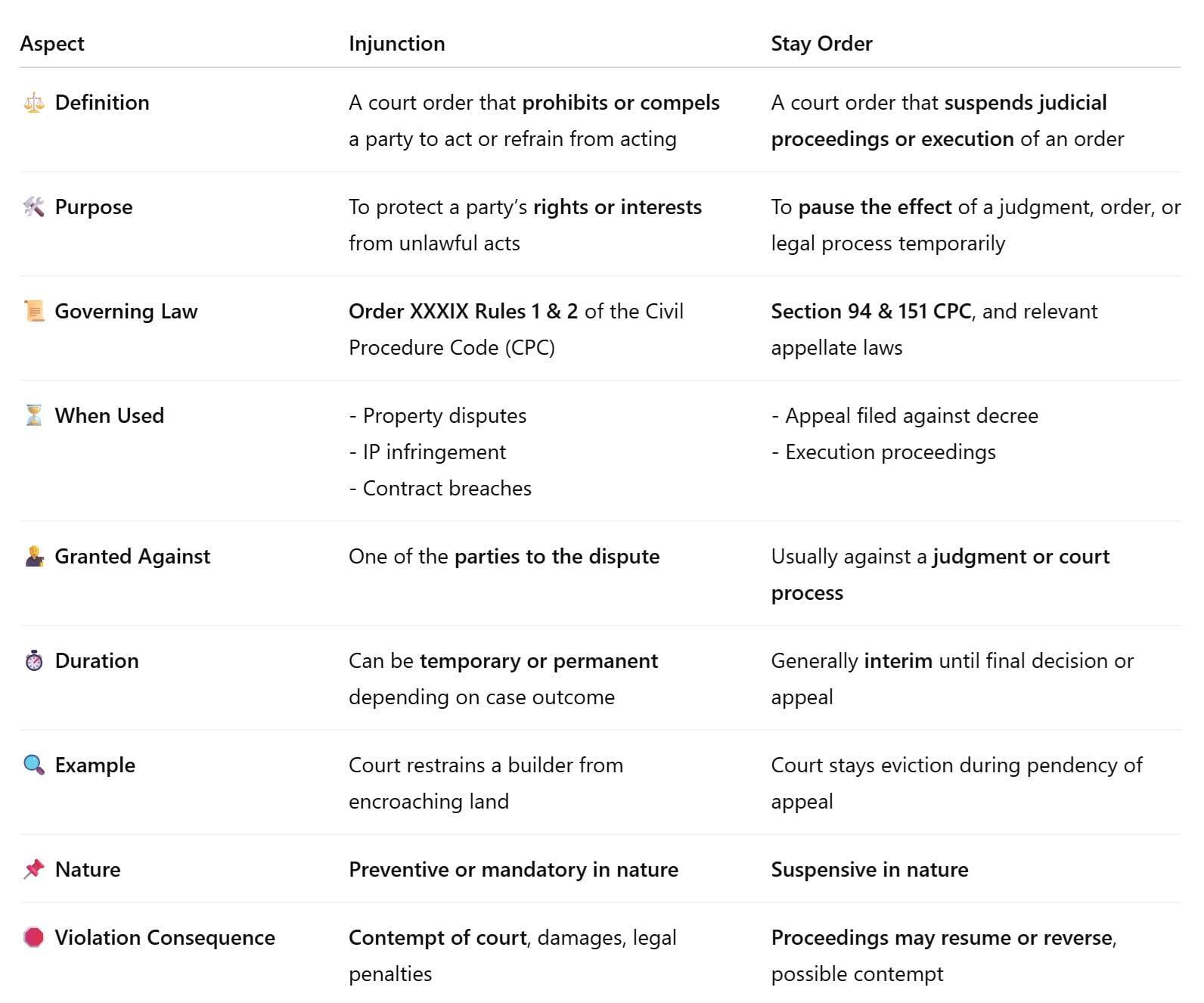
🧠 Difference Between Stay Orders and Injunctions
Though often used interchangeably, Stay Orders and Injunctions are legally distinct remedies, each serving different purposes under Indian law. Understanding the difference is crucial when deciding the appropriate course of action in a legal matter.
🧾 In Simple Terms: Injunction = Don't Do This / Do This & Stay Order = Put This on Hold
🧑⚖️ At TAXAJ:
We advise clients on whether to seek a stay or an injunction depending on the legal scenario, urgency, and jurisdiction — ensuring the right remedy at the right time.
📌 Recent Legal Precedents on Injunctions
Injunction law continues to evolve through landmark judgments that shape how courts view urgency, irreparable harm, and balance of convenience. Here are some recent and notable Indian legal precedents related to injunctions:
⚖️ 1. Zenith Computers Ltd. v. Jyoti CNC Automation Ltd.
(Bombay High Court, 2023)
Held: The court reiterated that an injunction will not be granted if the plaintiff fails to establish a prima facie case or delays filing the suit.
📌 Key Principle: Mere apprehension or speculative harm does not warrant injunctive relief.
⚖️ 2. PhonePe Pvt. Ltd. v. BharatPe
(Delhi High Court, 2022)
Held: Refused to grant interim injunction against use of the suffix ‘Pe’ citing co-existence and descriptive usage.
📌 Key Principle: Trademarks must be distinctive; common or generic elements may not attract injunction.
⚖️ 3. Ramesh Kumar v. Union of India
(Supreme Court, 2021)
Held: Injunctions against public authorities must show compelling public interest and cannot be issued to paralyze governance.
📌 Key Principle: Public interest and balance of convenience must be strictly weighed when restraining government actions.
⚖️ 4. Tata Sons Pvt. Ltd. v. Hakunamatata Tata Founders
(Delhi High Court, 2020)
Held: Granted permanent injunction against misuse of the TATA mark, even for parody accounts on social media.
📌 Key Principle: Reaffirmed brand protection via injunction even in digital spheres.
⚖️ 5. M. Gurudas & Ors. v. Rasaranjan & Ors.
(Supreme Court, 2020)
Held: Injunctions will not be granted if there is suppression of material facts or misrepresentation.
📌 Key Principle: Clean hands doctrine is vital — no relief if the applicant is dishonest or conceals information.
🔍 Summary of Legal Trends:
Courts now scrutinize urgency and clean hands more strictly.
Digital IP and brand protection cases are increasingly common.
Injunctions are rarely granted ex parte unless there is proven urgency and irreparable harm.
Courts emphasize balance of convenience and public interest over individual harm.
Why Choose Us?
At TAXAJ, we approach Litigative matters with a unique blend of legal expertise, emotional intelligence, and procedural precision. Such matters are highly sensitive and complex, requiring not just legal capability but also deep empathy, discretion, and smart advocacy. Here's why clients trust TAXAJ:
Consult us today to protect your legal rights and move forward with confidence.
✅ Protect Your Rights, Claim What's Rightfully Yours
If your contract has been breached, don’t absorb the loss in silence. Let TAXAJ help you pursue the compensation you deserve, with a legally strategic and commercially sound approach.
💬 Schedule a consultation today to discuss your damages or breach claim.

