Conversion of Proprietorship Firm to Private Ltd Company
A sole proprietorship cannot get all benefits of operation as it grows. So, there will be a need to convert the proprietorship into a private limited company. The conversion can bring in its wake all the benefits of a company like higher capital, limited liability, and so on. Conversion of a proprietorship into a private limited company provides many benefits, but it also brings along the diffusion of power and loss of independence. Therefore the decision must be taken after careful consideration of all the factors involved and see if it genuinely brings about privileges intended.
Get your private limited company registered in the fastest possible manner.
It usually takes 7 to 10 working days.
- DSC (2 nos)
- Filing of SPICe+ Form
- Issue of Incorporation Certificate along with PAN and TAN
- Includes Govt Fees & Stamp duty for Authorised Capital upto Rs. 1 Lakh except for the states of Punjab, Madhya Pradesh and Kerala
- Excludes foreign national / Body Corporate as director or business needing RBI/SEBI approval
- Assistance in Opening Bank Account
- Businesses looking to expand or scale operations on higher level
- Startups looking to raise capital and issue ESOPs
- Businesses looking to convert their existing firm structure into private limited company
- Businesses aiming to work globally or with reputed clients
DSC Application
Name approval form filing
Preparation of Incorporation Documents
Getting those docs signed by the respective stakeholders
Filing of e-Forms with ROC
Receipt of Incorporation Certificate with PAN, TAN, GST, EPF, ESI & Bank Account.
Name, Contact Number and Email Id of all the Stakeholders.
Directors Identification Number, if already.
Self Attested PAN, Aadhar & Passport size photo of all the Stakeholders.
Apostilled Passport, Mobile Bill and other KYC docs in case of NRI Stakeholder.
Latest Month Personal Bank statement of all the Stakeholders.
Specimen Signatures of all Stakeholders.
Few Proposed Business Names along with Objects.
Latest Electricity Bill/Landline Bill of Registered Office.
NOC from owner of registered office, If Owned. (Download Template)
Rent Agreement from Landlord, If Rented/Leased. (Download Template)
Brief description of main business activities of the proposed Company.
Shareholding pattern (50:50 or 60:40) between the Stakeholders.
Authorised & Paid Up Share Capital of the Company.
Everything you need to know about Conversion of Proprietorship to Private Limited Company!
Proprietorship vs Private Limited Company
Proprietorship vs Private Limited Company
A private limited company offers a lot of advantages over the sole proprietorship form of business. We have listed a few of them below:
- A sole proprietor would be incurred with unlimited liabilities for any losses incurred, which means that he/she will be required to pay personally for any losses incurred by the firm. The regulation of a private limited company makes a distinction between the owner and the entity, thereby making his/her liabilities limited.
- Sole proprietors will be taxed on their personal income tax rate, which isn’t the case with a private limited entity. Know more about income tax rate for companies.
- Sole proprietorship firms are not vested with adequate fund-raising options, in contrast to a private limited entity.
- The demise of a sole proprietor would lead to the closure of the firm, whereas a private limited Company facilitates the legal heirs to rightfully take over the affairs of the business.
Points of Difference between Proprietorship & Private Limited
| Sl. No. | Point of Difference | Proprietorship Firm | Private Limited |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Registration | No Formal Registration | A Private Ltd Company is registered under Companies Act,2013 |
| 2 | Legal Entity Status | Does not hold any Separate Legal Entity. | Hold separate Legal entity under the Companies Act, 2013 |
| 3 | Transferability of Shares | Non Transferable | Shares can be transferred |
| 4 | Liability | Unlimited | Limited to extend of shares |
| 5 | Members | Minimum - 1 Member Maximum – 1 Member | Minimum - 2 Member Maximum – 200 Member |
| 6 | Taxation | Owners Income Tax | Profits are taxed at 30% plus surcharges and cess as applicable |
| 7 | Compliance | Not Required | Annual Return, Annual Accounts required to be filed with the Registrar of Companies every year. |
Conditions for Conversion from Proprietorship to Private Limited
Conditions for Conversion from Proprietorship to Private Limited
- A takeover agreement or sale agreement needs to be entered into between the sole proprietor and company.
- The Memorandum of Association (MOA) needs to carry the object “The take over of a sole proprietorship”.
- All the assets and liabilities of the sole proprietorship must be transferred to the company.
- The shareholding of the proprietor should not be less than 50% of the voting power, and the same must continue to be held for a period of 5 years.
- The proprietor does not receive any additional benefits either directly or indirectly, except to the extent of shares held.
Initiating the Process of Conversion from Proprietorship to Private Limited
A sole proprietorship can be converted if the above-mentioned conditions are met. Talking about the conversion process, the following measures must be initiated by an entrepreneur to get the proprietorship firm converted into a private company:
- Obtaining the Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and Director Identification Number (DIN) for the sole proprietor and new director.
- Acquiring permission for naming the company, the application for which must be made in Form-1. Click here to check company name availability.
- Apply to MCA for Incorporation of company.
- Completing the slump sale formalities
- Modifying details of the bank account in accordance with the conversion.
- Submitting the relevant documents and forms (covered separately).
Procedure for Conversion of Proprietorship to Private Limited
Procedure for Conversion of Proprietorship to Private Limited
The following are the steps involved in the conversion of a proprietorship to a company when the above mentioned requirements are met:
- The proprietor must complete the slump sale formalities.
- The Director Identification Number (DIN) and the Digital signature certificate (DSC) must be obtained for all the directors.
- The proprietor must apply for the availability of name in Form – 1.
- Prepare the MOA and Articles of Association (AOA) of the company specifying the objects and the rules of the company.
- Apply for the incorporation of the company to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Submit all the relevant documents.
- Receive the Certificate of Incorporation.
- Apply for a new PAN and TAN.
- Modify the bank details as per the conversion.
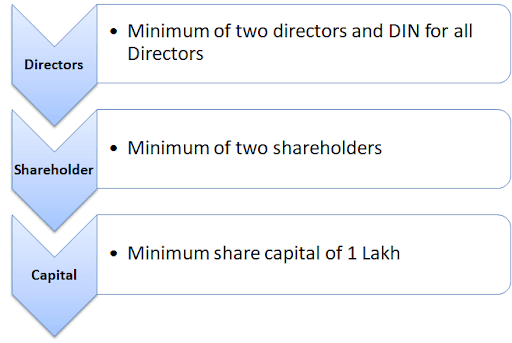
Prerequisites For Forming a Private Limited Company
Prerequisites For Forming a Private Limited Company
To form a private limited company from a sole proprietorship, the procedure is to first form the private limited company and then take over the sole proprietorship through a Memorandum Of Association (MoA) and transfer all benefits and liabilities to the limited company. So, the following requirements must be taken care of before applying for a certificate of incorporation.
- Directors: For the formation of a private limited company minimum of two directors are required. One of them can be the proprietor himself, and the other can be any relative or friend.
- Director Identification Number: The directors need to have an Identification Number as a prerequisite to incorporation.
- Shareholders: The company needs to have a minimum of two shareholders, and they can be the same as the directors. The owner of the sole proprietorship needs to be one of the directors of the limited company.
- Capital: The company needs to have a minimum authorised capital of 1 Lakh rupees.
Benefits of Conversion from Proprietorship to Private Limited
Benefits of Conversion from Proprietorship to Private Limited
- Capital expansion: A sole proprietorship is limited to the capital of the owner, whereas the private limited company has fundraising options and can raise higher capital for expansion.
- Limited liability: A sole proprietor is wholly responsible for the losses, and his/her personal assets will also get attached to repay creditors in case of losses. However, in case of a private limited company, such liabilities are limited by shares or warranty.
- Continuity: A sole proprietorship is dependent on a single person, so its existence is limited to that of the proprietor’s ability to operate. Whereas, the private limited company is a separate legal entity and not bound by the existence of a single owner.
Certificate of Incorporation for Converted Private Limited Company
After the completion of all the procedures specified above, the MCA validates the prescribed compliance requirements. If the administering body finds it satisfactory, the entity will be provided with a Certificate of Incorporation, which effectively gives birth to a new private limited company.
To convert a proprietorship into a private limited company, get in touch with a TAXAJ Advisor at connect@taxaj.com

