External Commercial Borrowing (ECB)
Unlocking Global Capital for Indian Businesses
External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) refers to the borrowing of funds by eligible Indian entities from non-resident lenders in foreign currency. Governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999 and regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), ECB serves as a key route for Indian companies to access low-cost capital from international markets for growth, expansion, or refinancing.
✅ Who Can Raise ECB in India?
Under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, and RBI’s ECB guidelines, the following Indian entities are eligible to raise ECB:
🏭 Companies in Manufacturing & Infrastructure Sectors
🌐 Indian Entities with Foreign Equity Participation

⚠️ Ineligible Borrowers Include:
💻 Software and IT-Enabled Services Companies
✅ Export-driven IT/ITeS companies needing global expansion or tech upgrades
🏦 Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
💰 Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
🏗️ Housing Finance Companies (HFCs)
🚀 Startups
🏫 Educational Institutions and Hospitals
🏢 SEZ Units
🧾 Holding Companies / Core Investment Companies (CICs)
🌍 Eligible Lenders under ECB Guidelines
External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) must be raised from recognized lenders, as defined and permitted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The eligibility of lenders is critical to ensure transparency, legitimacy, and regulatory compliance in cross-border borrowing. The following categories of overseas entities and institutions are considered eligible:
1️⃣ International Banks
Reputed foreign commercial banks that operate under proper regulatory supervision in their home countries are allowed to lend to Indian entities. These include:
Global commercial banks (e.g., HSBC, Standard Chartered, Citi)
Investment banks with lending arms
✅ Key Conditions for Lenders:
⚠️ Not Recognized as Lenders:
TAXAJ can assist you in verifying the credibility of foreign lenders, ensuring that your ECB proposal is fully aligned with FEMA and RBI regulations, and in completing all documentation, including lender declarations and KYC checks.
2️⃣ Multilateral and Regional Financial Institutions
Institutions involved in development financing and intergovernmental cooperation can act as lenders. Common examples include:
International Finance Corporation (IFC)
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
World Bank (IBRD)
European Investment Bank (EIB)
3️⃣ Export Credit Agencies (ECAs)
ECAs are government-backed institutions that provide credit or guarantee to exporters and investors. ECB can be raised through loans or buyer's credit supported by ECAs such as:
Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM)
Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC)
UK Export Finance
4️⃣ Foreign Equity Holders
Foreign shareholders holding a minimum equity stake (as defined by RBI) in the Indian borrower are eligible lenders. This facilitates:
Intra-group funding
Strategic capital infusion
Parent-subsidiary funding relationships
📌 Equity Threshold:
Minimum 25% direct equity holding (for automatic route eligibility)
5️⃣ Overseas Branches and Subsidiaries of Indian Banks
These are permitted to participate as ECB lenders only under the approval route and subject to prudential norms laid down by the RBI. Their participation is typically regulated to prevent round-tripping and maintain capital adequacy.
6️⃣ Foreign Institutional Investors / Pension Funds / Insurance Funds
Subject to RBI and SEBI regulations, some institutional investors with a long-term investment outlook may also qualify to lend via ECBs, especially for infrastructure projects.
7️⃣ Exporters and Foreign Collaborators
Where trade credit or deferred payment arrangements are involved, international vendors or technology collaborators may lend through structured ECB instruments, depending on the purpose and sectoral guidelines.
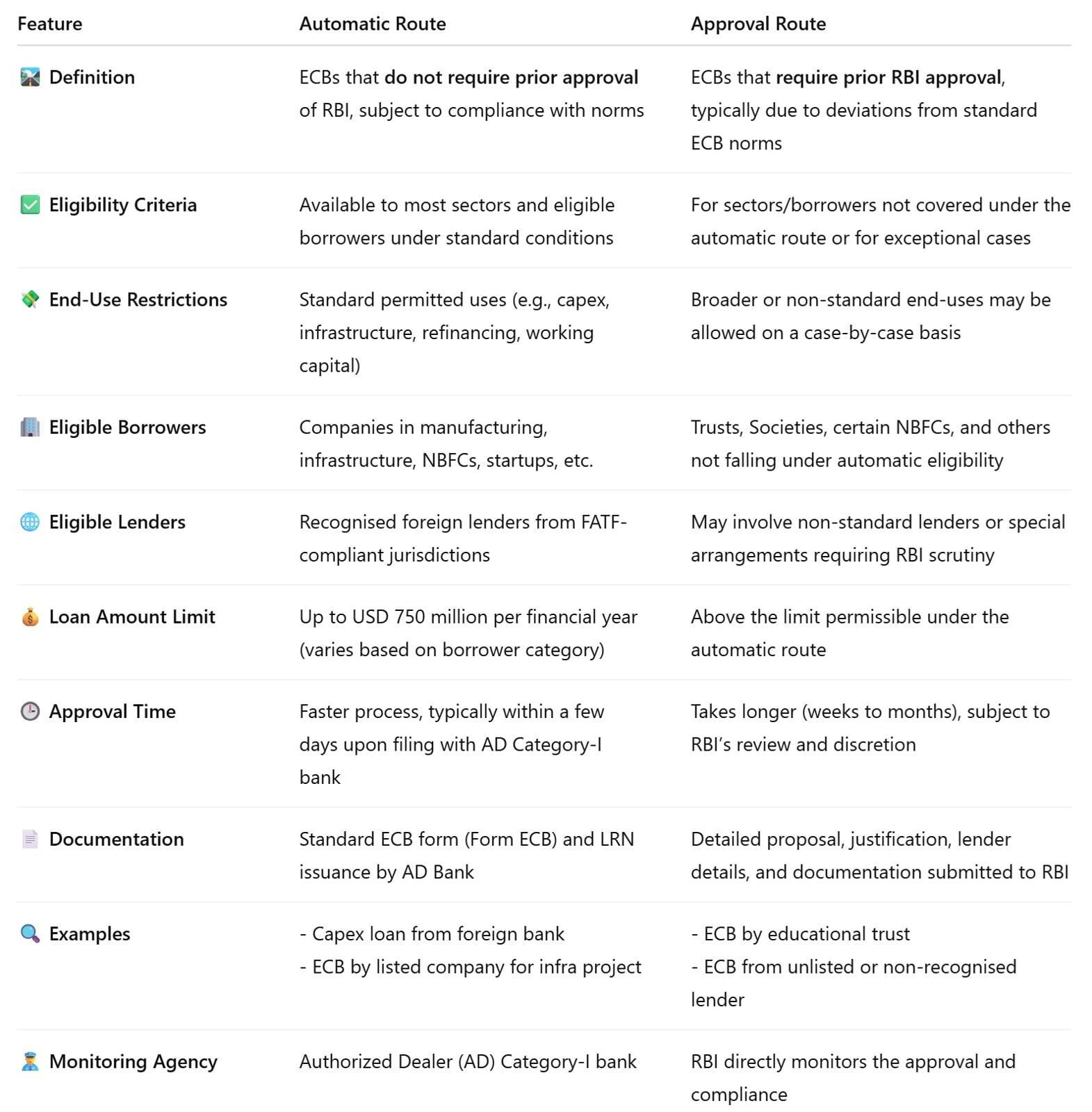
🔄 ECB Routes: Automatic vs. Approval Route
📋 End-Use Restrictions under ECB Guidelines
✅ Permitted End-Uses (Allowed under Both Routes)
Indian borrowers can use ECB proceeds for the following approved purposes under the Automatic Route (and Approval Route where applicable):
Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
Purchase of plant, machinery, or equipment
Expansion of manufacturing units
Construction of infrastructure projects
Infrastructure Development
Roads, ports, airports, power plants, and urban transport
Social infrastructure like hospitals, educational institutions
Refinancing of Rupee Loans
Refinancing of existing ECBs or domestic rupee loans for capex
Subject to certain conditions (like average maturity requirements)
Working Capital & General Corporate Purposes
Allowed for specific eligible borrowers such as NBFCs or infrastructure companies
Subject to sector-specific guidelines
Import of Capital Goods / Equipment
Especially when importers avail of deferred payment arrangements
On-Lending to Infrastructure or Housing Sector
NBFCs can use ECBs to on-lend to eligible segments within prescribed norms
Innovative Sectors / Startups
Startups are permitted to use ECBs for a broader range of business needs under relaxed norms
🔍 Special Cases – Conditional Usage:
Some uses may be permitted under the Approval Route or subject to additional compliance:
Working capital for general corporate purposes (in select sectors)
Overseas acquisition or expansion (requires special RBI clearance)
Bridge finance for IPOs or FDI-linked activities (only in regulated environments)
🛡️ Why End-Use Restrictions Matter
❌ Prohibited End-Uses (Not Allowed)
The RBI prohibits using ECB proceeds for the following purposes, even under the Approval Route:
Real Estate Activities
Includes buying/selling land or real estate (except for affordable housing or construction of specific infrastructure)
Investment in Capital Market Instruments
IPOs, mutual funds, stock purchases, derivatives, etc.
Equity Investment in India
ECB proceeds cannot be used to invest in equity or to fund acquisition of shares
Working Capital (for General Borrowers)
Except under specific categories like NBFCs and infrastructure firms
Repayment of Existing Rupee Loans (Except in Specific Cases)
Not permitted unless within permitted refinancing structure
Use by Individuals
Individuals (as borrowers or end-users) are not permitted to raise or utilize ECB
Purchase of Land for Real Estate, Agriculture, or Trading
Strictly restricted regardless of borrower type

TAXAJ assists in reviewing your ECB proposal, mapping your business requirement against RBI’s end-use guidelines, and structuring compliant usage strategies for efficient capital deployment.
📋 End-Use Restrictions under ECB Guidelines
Understanding the structural framework around External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) is essential for businesses looking to raise capital from overseas. The RBI governs ECBs through specific regulations that define how long the loans can last (tenure), how much they may cost (interest and charges), and how much a borrower can raise (limits).
⏳ ECB Tenure (Maturity Period)

💸 2. ECB Cost (All-in-Cost Ceiling)

📊 3. ECB Limits (Borrowing Caps)

🧮 Important Compliance Notes:
🛡️ TAXAJ’s Role in ECB Structuring
TAXAJ assists in:
Structuring the ECB to meet maturity and cost compliance
Calculating and negotiating all-in-cost terms
Filing applications with RBI and obtaining LRN
Ensuring correct documentation and ongoing reporting
📊 Reporting & Compliance
Borrowers must adhere to various compliance and reporting requirements:
ECB-1: Filing with AD bank at the time of drawdown
Loan Registration Number (LRN): Issued by RBI before remittance
ECB-2 Return: Monthly reporting of transactions
Annual Performance Reports (APR) for ODI-linked ECBs
End-use certificates from chartered accountants
⚖️ Why ECB Compliance is Crucial
💼 How TAXAJ Can Help You
TAXAJ offers end-to-end advisory and compliance support for External Commercial Borrowings:
📊 Feasibility study & ECB structuring
✍️ Drafting loan agreements and documentation
🏦 Liaising with RBI and Authorized Dealers (AD Banks)
🧾 Assistance with ECB-1, ECB-2, LRN, and end-use reporting
📤 Filing under approval route, if required
🔁 Restructuring and refinancing of existing ECBs
🕵️♂️ FEMA and RBI audit support
🌟 Why Choose TAXAJ for Your ECB Needs?
📞 Ready to Raise Capital Globally?
Reach out to TAXAJ to ensure your ECB is strategically structured, legally compliant, and aligned with your business objectives.
for a Company Law matter of NCLT case review or consultation....

