Golden Rules of Accounting – Overview & Types

Every economic entity must present its financial information to all its stakeholders. For this presentation, it must account for all its transactions. Since economic entities are compared to understand their financial statuses, there has to be uniformity in accounting. To bring about uniformity and to account for the transactions correctly there are three Golden Rules of Accounting. These Golden rules of Account form the very basis of accounts in fact passing journal entries which in turn form the basis of accounting golden rules and bookkeeping.
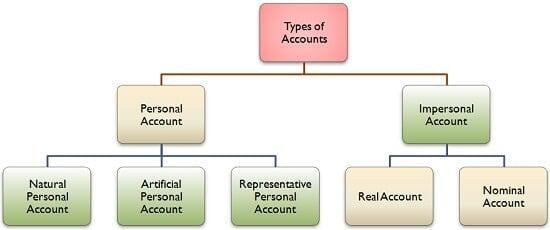
Types of Accounts
To understand the Golden Rules of Accounting we must first understand the types of accounts.
Real Account
A Real Account is a general ledger account relating to Assets and Liabilities other than people accounts. These are accounts that don’t close at year end and are carried forward.
Personal Account
A Personal account is a General ledger account connected to all persons like individuals, firms and associations. There are certain examples of Personal account
Nominal Account
A Nominal accounts is a General ledger account pertaining to all income, expenses, losses and gains.
Golden rules of accounting
Looking at the nature of all the accounts, the accounting rules have been devised. For each account there is a set of Golden Rules and hence there are three Golden Rules of Accounting.
Illustration
An entity named Orange Ltd. has the following transactions.
- It deposits Rs.10,000 into Bank
- It buys goods worth Rs.50,000 from Apple Ltd.
- It sells goods worth Rs.35,000 to Melon Ltd.
- It pays Rs.12,000 as Rent for its premises
- It earns Rs.3,000 as interest on bank account.

| Transaction | Accounts involved | Type of Accounts |
| Deposit Rs.10,000 in Bank | Bank Account Cash Account | Real Account Real Account |
| Purchase goods worth Rs.50,000 from Apple Ltd. | Purchase Account Apple Ltd. Account | Nominal Account Personal Account |
| Sale of goods worth Rs. 35,000 to Melon Ltd. | Sales Account Melon Ltd. Account | Nominal Account Personal Account |
| Pays Rs.12,000 as rent | Rent Account Bank Account | Nominal Account Real Account |
| Earn Rs.3,000 as interest on Bank account | Interest received Bank Account | Nominal Account Real Account |
Now applying the golden rules to each of the transactions we will get the following journal entries :
- Deposit Rs.10,000 in Bank
Both Bank and Cash are real accounts and so the Golden rule is:
- Debit what comes into the business
- Credit what goes out from the business
So the entry will be:
| Bank A/C | Dr. | 10,000 | |
| To Cash A/ C | 10,000 |
- Purchase goods worth Rs.50,000 from Apple Ltd.
The Purchase Account is a Nominal account and the Creditors Account is a Personal account.
Applying Golden Rule for Nominal account and Personal account:
- Debit the expense or loss
- Credit the giver
The entry will be:
| Purchase A/C | Dr | 50,000 | |
| To Apple Ltd. A/C | 50,000 |
- Sale of goods worth Rs.35,000 to Melon Ltd.
The sale account is a Nominal account and the Debtors Account is a Personal account.
Hence the Golden Rule to be applied is:
- Debit the receiver
- Credit the income or gain
Thus the entry will be:
| Melon Ltd. A/C | Dr | 35,000 | |
| To Sales A/C | 35,000 |
- Pays Rs.12,000 as rent
Rent is a Nominal account and Bank is a real account.
The Golden Rule to be applied is:
- Debit the expense or loss
- Credit what goes out of business
The entry thus will be:
| Rent A/C | Dr. | 12000 | |
| To Bank A/C | 12000 |
- Earn Rs.3,000 as interest on Bank Account
Interest and Bank are Nominal account and Real Account.
The Golden rule to be applied is:
- Debit what comes into the business
- Credit the income or gain
Hence the entry will be:
| Bank A/C | Dr | 3,000 | |
| To Interest Received A/C | 3,000 |
Golden rules of accounting are the basic accounting rules on the basis of which accounting entries are recorded.
Personal Account:
Real Account:
Nominal Account:
The rule related to nominal account states that debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains. In other words, if any expense or loss is incurred for the business, expense or loss account shall be debited and if any income or gain is earned in business, income account or gain/profit account shall be credited.
For example: If salaries are paid to employees then salary is an expense and hence salary account shall be debited. Likewise any rent received shall be credited to rent account as it is an income.
Modern Rules of accounting (Classification of Accounts):As per modern rules of accounting, transaction will be categorised into 6 heads or accounts and any increase or decrease in such account will either be debited or credited in the manner shown in the table given below:
Types of Account | Account to be debited | Account to be credited |
Assets account | Increase | Decrease |
Liabilities account | Decrease | Increase |
Capital account | Decrease | Increase |
Revenue account | Decrease | Increase |
Expenditure account | Increase | Decrease |
Withdrawal account | Increase | Decrease |
B (Debtor) AccountDr.
To Sales Account
(Being goods sold to B on credit)
Hence, it can be concluded that accounting rule is basis of accounting. Once a transaction has been done, it shows how that transaction should be recorded in the books.
Conclusion
To summarize, all transactions of an entity must be accounted for. To account these transactions the entity must pass journal entries which will then summarize into ledgers. The journal entries are passed on basis of Golden Rules of accounting. To apply these rules one must first ascertain the type of account and then apply these rules.
- Debit what comes in, Credit what goes out
- Debit the receiver, Credit the giver
- Debit all expenses Credit all income
These are the foundation of accounting and hence are called the Golden Rules of accounting. They are like the letters of the English alphabet if one does know letters he cannot know words and hence cannot use the language. Similarly for accounting, if one does not know the golden rules, he cannot pass journal entries and hence won’t be able to know to account.

